Thinking About Grid-Tie Solar? Consider an Off-Grid Energy Storage Alternative or Add Storage to an Existing Grid-Tie System
There are many practical reasons to install a grid-tie or an off-grid solar energy system. Each meets a specific set of customer goals.
- Save money
- Reduce or eliminate your utility bill
- Take advantage of tax credits and incentives
- Increase property values
Each of these goals is highly appealing and can be achieved with a grid-tie or off-grid system. However, battery storage allows you to achieve the added benefits of:
- Complete off-grid energy independence
- Operate indefinitely when the grid goes down
- Reduced insurance premiums
What are these systems, how do they provide these benefits, how does battery energy storage fit into the equation and how do you get started?

What is Grid-Tie Solar?
A grid-tie system consists of solar panels and a grid-tie inverter to connect to the electricity power grid. This is the utility company. The system relies on the grid/utility company in order to produce usable energy from solar panels, funnel excess energy for net metering, and to obtain clean energy credits or for later usage. Most solar panel systems are grid-tied to the utility company electricity feed through your meter connection.
Grid-tie Advantages
- A simple grid-tie system may be a lower upfront expense. It does not require battery equipment and the higher power inverters that off-grid systems do.
- Customers may take advantage of net metering. Save money while ensuring your energy is never wasted.
- You’re helping to improve the efficiency of the main electrical grid during peak usage times.
Grid-tie Disadvantages
- If the utility goes down, your grid-tie system will shut off in order to prevent energy from feeding into the system and potentially harming utility workers. Adding a backup battery to your grid-tie system will allow you to have limited power for a short period of time for a few circuits - typically 5 - 6 hours.
- Installing grid-tie solar may not be feasible in remote or undeveloped areas without nearby power lines.

What is Off-Grid Solar?
Off-grid solar is a system of solar panels, a battery energy storage system (BESS) and no grid-tie.
With an off-grid system you make and use your own electricity. You can still have a connection to the grid as a backup if the solar panels and batteries cannot meet your electrical demands. The grid will always be there in case you need it.
A properly designed off-grid system can power your home for decades without using grid power.
Off-Grid Advantages
- Keep your home or business powered when the grid goes down or by using solar panels.
- All-in-one design can make off-grid systems less complex than grid-tie systems to install.
- Depending upon your energy consumption, the actualized cost is about half that of a grid-tie system. Lowering your energy consumption and then adding an off-grid system will lower your monthly utility costs.
- Own the equipment, at a very low cost, usually less than half the electric bill.
-
Off-Grid Disadvantages
- Utilities may present roadblocks to obtaining off-grid solar permits since the energy is not being sent back into the grid.
- As with all energy storage systems, batteries must be disposed of at the end of their lifecycle, 10 - 15 years typically for lithium iron phosphate batteries.
- Requires more solar panels than a grid-tie system.
What is a BESS?
The battery energy storage system (BESS) is equipment that stores energy in batteries, which is used later to keep the power on and for electricity cost savings.
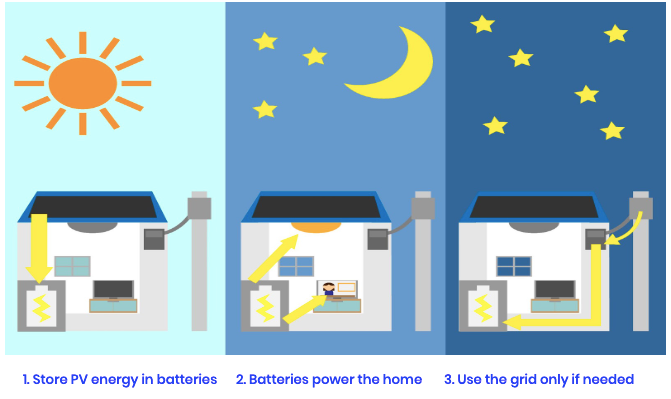
- A BESS stores energy from solar panels and converts it to AC power to run appliances.
- A BESS can prioritize solar, battery, and generators to provide power so that the grid becomes the backup source.
- A BESS can run heavy loads such as air conditioning, hot water heaters and EV charging stations without support from the grid.
Are There Tax Credits for Installing Battery Systems?
You may be eligible for federal, state or local tax credits and incentives. We recommend contacting your utility or a certified public accountant who can advise you on your eligibility for these incentives. The Database of State Incentives for Renewables and Efficiency website https://www.dsireusa.org/ is a resource that can be consulted for programs that apply to you.
Determining your Financial Savings
What Does it Cost?
Whether you choose grid-tie, off-grid or grid-tie with a BESS, you may be driven by the financial goal of eliminating your utility bill.
Grid-tie incentives are numerous and grid-tie is the system of choice for utilities. The job of a grid-tie system is to connect to the grid to supplement the utility electrical feed. This fits within the model of how a utility generates and delivers electricity to consumers, which is based upon perceived usage patterns. Thus, the up front costs are lower than off-grid and are amortized over the life of the contract, which can be 40 or more years.
Off-grid systems have a higher up front cost because they are not subsidized by the utility. An off-grid system can be financed at a monthly rate that is half your monthly energy savings and can be paid for within 10 years.
If you’ve met your financial savings goals, then the system has been successful in providing value.
Which Part of My Electric Bill Can I Eliminate?
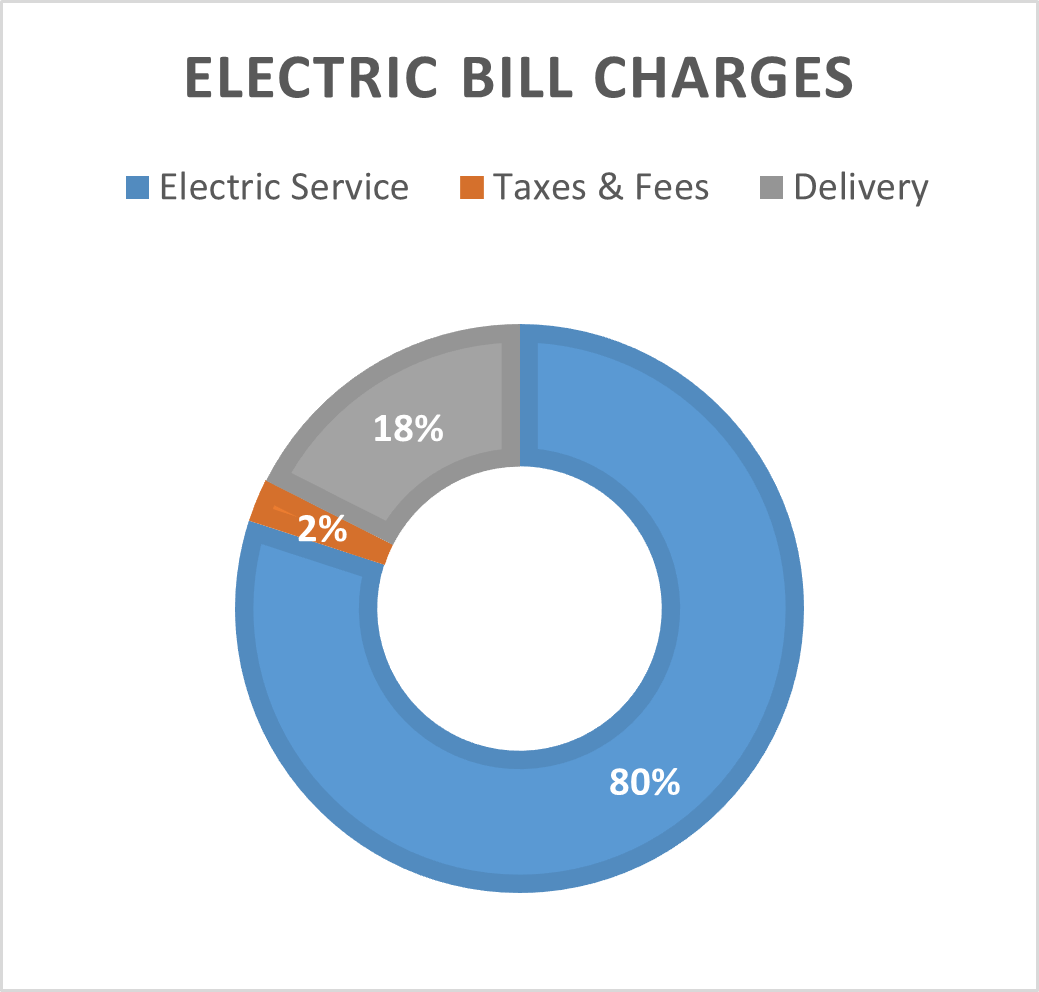
A typical electricity utility bill is broken into the following charges:
- Electricity Supply Service
- Generation Services
- Fuel Factor @ $0.0XXX per kWh
- Transmission Services
- Distribution Services
- State Electric Consumption Tax
- Local Consumers Tax
- Universal Service Fee
80% of your bill is the electric supply service fee. This fee pays for the utility to generate electricity and electricity distribution (via local wires to your home). This fee can be eliminated. The remaining portions of your bill, delivery (Transmission Services and Universal Service Fee @ 18%) and Taxes & Fees (2%) must be paid whether you use electricity or not.
How do I Get Started - What is Next?
You’ve read this guide, you’ve determined your cost saving and energy goals and now you know what you want: grid-tie, off-grid BESS or a grid-tie with BESS. What’s next?
Whether you manage the project yourself or find an installer who can put it all together, the following steps will get you from idea to completion and are a part of each installation:
Feasibility Study - This is the first step in the process. The feasibility study ensures that your project is carefully planned to cover all of your energy requirements. It includes: energy audit, which utility and government incentives apply, number of panels needed to get your electric bill to zero, and if off-grid, number of panels needed to run your home and store energy to your batteries at the same time.- Site Survey - A site survey takes the feasibility study results and applies them to your environment to show where everything will be installed. It includes: site evaluation, measurements, roof type, irradiation mapping, and site azimuth.
- Engineering - For the engineering phase of the project, a project engineer will design the racking, power conversion equipment, wiring, necessary electrical service upgrades, surge suppression and other equipment needed to build your system.
- Permitting - Permits required to install panels on your roof and other power equipment are identified and obtained for your project.
- Installation - This is the physical placement of the solar racking, solar panels, and power conversion system.
- Electrical Work - A bonded electrician is used to connect the power conversion system, manual bypass switch, surge suppression and wiring into your electrical service.
Conclusion
Going solar provides many financial advantages to the consumer and helps to achieve the goal of energy decarbonization and making our planet healthier. When the utility grid goes down, your grid-tie system will shut off and your house or business will NOT have power.
If you have a BESS when the utility grid goes down, you will keep your home or business powered.
Sol Donum™ is an engineering firm that designs and manufactures products for off-grid and grid-tie energy storage. Contact us today at
sales@soldonum.com or visit our website to learn more about how our
R-Power and
Vulcan technologies, and installation partners can support your off-grid or grid-tie design to save you money and keep your power on.
Glossary of Terms
AC - AC, also known as alternating current is a voltage that changes direction 60 times each second from negative to positive. This is what homes, businesses, hospitals, schools and safety services use for power.
BESS - Battery energy storage system (BESS) is a collection of equipment that stores energy in batteries and converts it to alternating current (AC), which is used later.
Distribution Services - The transformers and wires that connect homes and businesses to the utility’s transmission services.
Grid-Tie - Systems that add their alternating current (AC) outputs with the utility’s AC line to produce the desired total power.
Net Metering - If the amount of energy used by your home is less than the amount added to the grid, then the utility will credit you for the balance of the energy.
Off-Grid - Systems that store energy in batteries and send their AC outputs directly to the home or business. They do not add their AC output to the utility’s AC line.
Solar Panels - Photo-voltaic cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC). Power conversion equipment changes the DC output of the solar panels into alternating current (AC).
Transmission Services - The lines, towers and substations that carry electricity from the utility generators to local distribution services.
Utility - The entity that generates, transmits and distributes/furnishes electricity.
